Subtitle:
Improving Writing Skills: how to move up from the Elementary to the Intermediate Level using Adjectives.
If you are a teacher you would agree with me that helping students move from an Elementary Level to an Intermediate one takes time and practice. One does not acquire the level in one day, you need to go step by step and you’ll need to climb all the stairs to be successful, there is no lift here.
students move from an Elementary Level to an Intermediate one takes time and practice. One does not acquire the level in one day, you need to go step by step and you’ll need to climb all the stairs to be successful, there is no lift here.
When I mark their compositions some students find it difficult to understand why a composition with almost no mistakes deserves a Pass whereas another one with more “red” ink gets a better mark. Although I explain to them that you’re not only marked for grammatical mistakes and they seem to understand I thought it might be a good idea to do an experiment so that they could clearly see my point.
The little experiment was carried out during the last 20 minutes of the lesson after having dedicated most of the lesson to working with adjectives. The aim was letting the student see for themselves the difference, in terms of adequacy, between two or three grammatically correct sentences by voting on the best one. By letting them be the judges of the best sentence, they also become aware of why essays with no mistakes might score significantly higher or lower.
Before starting with the activities dedicated to Adjectives, I told my students that my aim on that day was to improve their writing skills to help them move from an Elementary Level to an Intermediate one. In my opinion, this bit of information before starting is essential to get their full attention!
Blog de Cristina is also on Facebook. Click to follow!
STEP 1. ORDER OF THE ADJECTIVES
Although not all grammarians agree on the order of the adjectives and the rules for adjective order are quite complicated, it is necessary to give them some kind of order they can stick to. I always use this sentence to help them remember

Important points:
1. Don’t overuse adjectives. While having two adjectives before a noun sounds natural, more than three would have the opposite effect.
2. Purpose adjectives go just before the noun: riding boots ( boots for riding), sleeping bags (bags for sleeping).
3. Numbers go before adjectives: three huge houses.
STEP 2. USING STRONG/EXTREME ADJECTIVES
Isn’t it true that when you cross out things like very furious, students invariably ask … but, “why can’t you say very furious??”
1. I find it important to see the before and the after. So, prior to beginning with step 1, show them an example of what they normally write, well, a bit exaggerated maybe 🙂 .
Last week I went to a very big beach. It was very hot and I was very angry because I couldn’t find a place to put my towel as it was very crowded. Finally, I saw one of my best friends and I managed to squeeze in next to her. We went for a walk but after half an hour I was very tired and very hungry so I bought a sandwich, but it tasted very bad. Oh My God !!!
1. Brainstorm extreme adjectives like angry-furious, small-tiny, big-enormous, dirty-filthy, happy-delighted, sure-positive…etc.
2. Point out you cannot use very with these adjectives, but “absolutely” or “really” -among others.
3. Practising intonation with extreme adjectives in dialogues is always an enjoyable activity! Even more fun if you give them the card and get them moving around the class and talking to different people. For this activity, I always use this handout from onestopenglish.com
4. That might be a good time to display the text above again so that they improve it using extreme adjectives.
STEP 3. WRITING GAME
Before the game: Write down on slips of papers, verbs that they have recently studied. For this exercise, I chose verbs with dependent prepositions. Put them in a bag or envelope.
Explain that this writing exercise is going to be a competition, where only sentences without grammatical mistakes are going to be shortlisted. These sentences will be read aloud and students will vote for the best one taking into account the length of the sentence, the use of adjectives before the noun and also the use of extreme adjectives
1. Students work in pairs competing for points against the other students in the class.
2. From the bag, ask a student -the innocent hand-to pull out a slip of paper containing a verb in the infinitive form.
3. Students have 2 minutes to write a good sentence containing the verb.
4. Quickly correct mistakes and put a tick to the ones being shortlisted.
5. Sentences are read aloud for students to choose the best one, which is awarded one point. The pair with the highest number of points wins.
At some point during the game, I make a point of telling students once again to reflect on why they feel some sentences are intuitively better.

Hope you find it useful!



 students move from an Elementary Level to an Intermediate one takes time and practice. One does not acquire the level in one day, you need to go step by step and you’ll need to climb all the stairs to be successful, there is no lift here.
students move from an Elementary Level to an Intermediate one takes time and practice. One does not acquire the level in one day, you need to go step by step and you’ll need to climb all the stairs to be successful, there is no lift here.

 If you think my blog deserves the award, please 1. Follow this link to their facebook ,
If you think my blog deserves the award, please 1. Follow this link to their facebook ,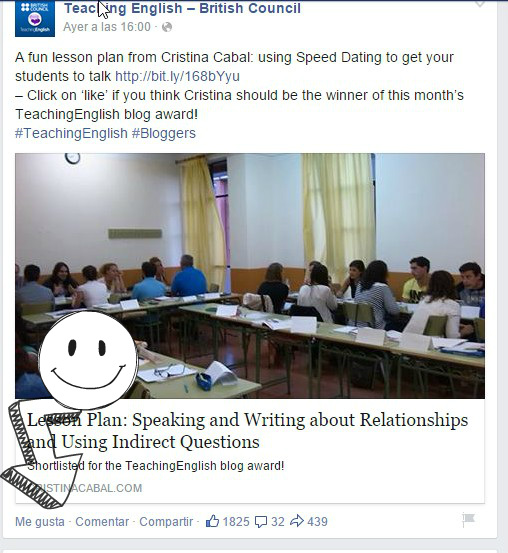 I’ll keep my fingers and toes crossed !! thanks in advance!
I’ll keep my fingers and toes crossed !! thanks in advance!